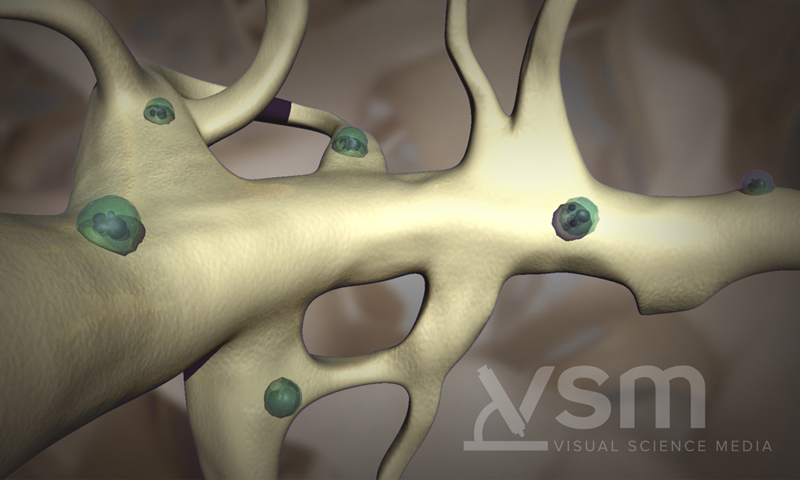
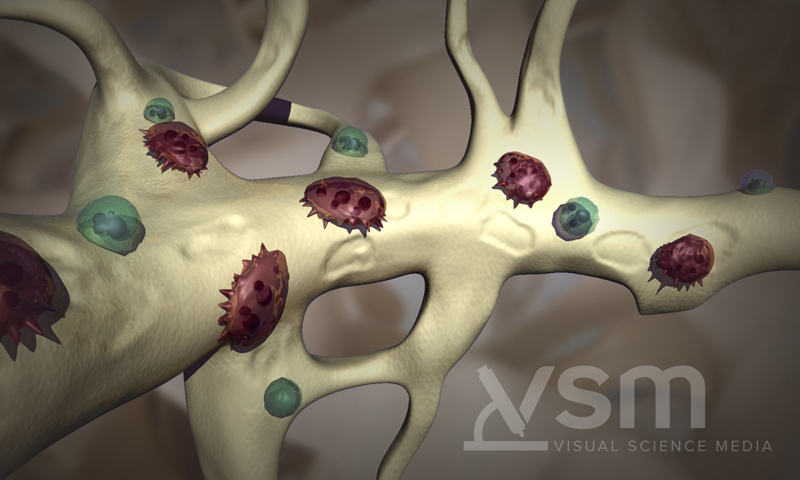
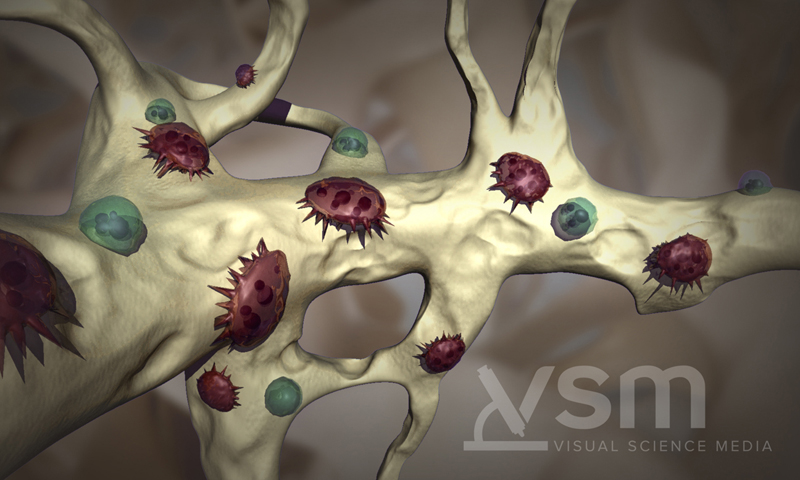
Bone destruction, caused by overactivity of osteoclasts, results in bone problems for over 80% of patients with multiple myeloma. Myeloma cells cause osteoclasts to accelerate bone destruction, while also interfering with osteoblasts receiving the signal to create new bone. Multiple myeloma cells adhere to the stromal cells in the bone marrow. This adherence results in a dysregulation of the cytokines that govern the bone remodeling process, leading to increased osteoclast activity and bone resorption.
Technology
Autodesk Maya, Adobe After Effects, Adobe Photoshop